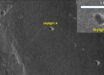
Astronomers using NASA’s Deep Space Network antenna have captured the first radar images of asteroid 2004 BL86, which made its closest approach January 26 at 11:19 a.m. EST (8:19 a.m. PST, 04:19 p.m. GMT, 05:19 p.m. CET, 09:49 p.m. IST) at a distance of 1.2 million km.

This image shows the asteroid 2004 BL86 and its small companion. Image credit: NASA / JPL-Caltech / Sci-News.com.
Asteroid 2004 BL86 (also catalogued as 357439) was discovered ten years ago by a telescope of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) survey in White Sands, New Mexico.
It is classified as an Apollo asteroid, a group of near-Earth objects (NEOs) whose orbits cross that of Earth.
The object is about 325 meters across and has a small asteroid moon 70 meters across.
In the near-Earth population, about 16 percent of asteroids that are about 200 meters or larger are a binary (the primary asteroid with a smaller asteroid moon orbiting it) or even triple systems (two moons).
The current flyby was the closest approach 2004 BL86 will make to Earth for at least the next two centuries.
NASA places a high priority on tracking asteroids and protecting Earth from them.
In fact, the United States has the most robust and productive survey and detection program for discovering NEOs.
To date, U.S. assets have discovered over 98 percent of the known NEOs.
In addition to the resources NASA puts into understanding asteroids, it also partners with other U.S. government agencies, university-based astronomers, and space science institutes across the country, often with grants, interagency transfers and other contracts from NASA, and also with international space agencies and institutions that are working to track and better understand these objects.
NASA’s Near-Earth Object Program manages and funds the search, study and monitoring of asteroids and comets whose orbits periodically bring them close to Earth.
In 2016, the agency will launch the OSIRIS-REx space probe to the asteroid (101955) Bennu, one of the most potentially hazardous of the known NEOs.
The mission will be a pathfinder for future spacecraft designed to perform reconnaissance on any newly discovered threatening objects.