Astronomers have confirmed three supernova remnants and discovered 16 new supernova remnant candidates in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small satellite galaxy of the Milky Way located about 160,000 light-years away.
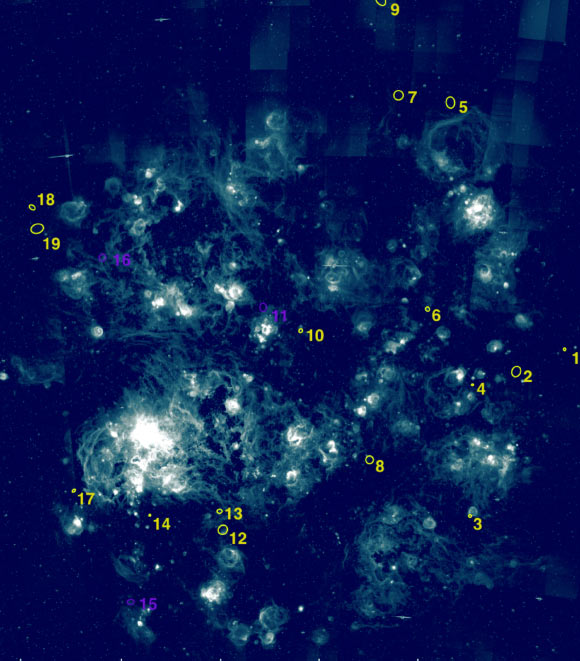
The positions of 16 new supernova remnant candidates in the Large Magellanic Cloud are marked in yellow; previously classified X-ray supernova remnants — MCSNR J0541-6659, MCSNR 0522-6740 and MCSNR J0542-7104 — are marked in violet color. Image credit: Yew et al., doi: 10.1093/mnras/staa3382.
“These supernova remnants were once young and bright stars,” said co-lead author Miranda Yew, a Ph.D. candidate at Western Sydney University.
“Their contemporaries from the central, dense part of the galaxy vanished a long time ago, as they merged into the vast interstellar medium.”
“However, these stubborn celestial objects managed to survive — this is because the conditions in the galaxy’s outskirts are far more favorable for a longer life.”
Using data from the Curtis Schmidt telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, Yew and colleagues found that the new supernova remnant candidates were over 230 light-years across — larger by a factor of two compared to other previously confirmed supernova remnants.
“Our analysis suggests we discovered a previously unknown class of large and predominantly optically visible supernova remnants,” Yew said.
“We believe these objects are mainly residing in a very rarefied environment and are up to 120,000 years old.”
“The rarefied environment allows the supernova remnants to expand with nothing to impede them.”
“Due to their age, radio emission particles can no longer be detected by even most sensitive instruments.”
The findings suggest the Large Magellanic Cloud is going through a period of recent star formation.
“We plan to further explore the supernova remnants in X-rays with eROSITA, a joint project with the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Farching, Germany,” the researchers said.
Their results appear in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
_____
Miranda Yew et al. 2020. New optically identified supernova remnants in the Large Magellanic Cloud. MNRAS 500 (2): 2336-2358; doi: 10.1093/mnras/staa3382