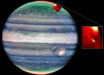
Galaxy clusters are some of the most massive structures that can be found in the Universe. A remarkable new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows RXC J0232.2-4420, a massive galaxy cluster located approximately 3.5 billion light-years away in the constellation of Eridanus.
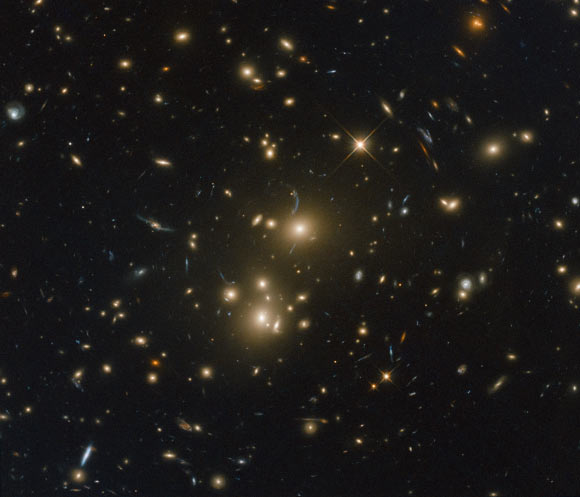

This Hubble image shows the massive galaxy cluster RXC J0232.2-4420. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / RELICS.
Galaxy clusters contain thousands of galaxies of all ages, shapes and sizes, together totaling a mass thousands of times greater than that of the Milky Way Galaxy.
At one point in time they were believed to be the largest structures in the Universe — until they were usurped in the 1980s by the discovery of superclusters.
However, clusters do have one thing to cling on to; superclusters are not held together by gravity, so galaxy clusters still retain the title of the biggest structures in the Universe bound by gravity.
The enormous gravitational influence of galaxy clusters distorts the space around them in such a way that they can be used as giant cosmic lenses that magnify distant background galaxies.
Studying some of the earliest galaxies in the Universe will tell astronomers more about our cosmic origins.
RXC J0232.2-4420 was featured in a study that focused on galaxy clusters that are especially luminous sources of X-rays.
The study searched for diffuse light around the brightest cluster galaxies, among the most massive galaxies in the Universe.
This diffuse light comes from intergalactic stars strung out between the constituent galaxies of the cluster and the aim of the study was to explore various theories for the origins of these stars.
One theory is that that may have been stripped from their host galaxies during mergers and interactions.
This image of RXC J0232.2-4420 was taken by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and Wide-Field Camera 3 (WFC3) instruments as part of an observing program called Reionization Lensing Cluster Survey (RELICS).
RELICS imaged 41 massive galaxy clusters over the course of 390 Hubble orbits and 100 Spitzer Space Telescope observing hours.