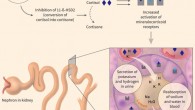
A new study by University of California, Irvine researchers has found that recreational ocean water exposure changes the human skin microbiome, and waterborne microbes persist on the skin for at least 24 hours. Swimming in the ocean alters the skin microbiome and may increase the likelihood of infection. Image credit: Pexels. Skin is the human body’s first line of defense, both physically and immunologically, against invading microorganisms and...