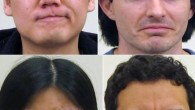
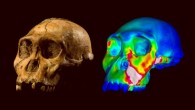
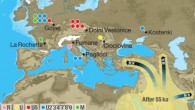
Analyses of genome-wide data from 51 Eurasians from 7,000 – 45,000 years ago reveal two big changes in prehistoric human populations that are closely linked to the end of the last Ice Age, approximately 19,000 years ago, according to an international team of researchers led by Harvard Medical School scientist Dr. David Reich. Mousterian Homo neanderthalensis by Charles R. Knight. “Archeological studies have shown that anatomically modern Homo...