Using observations with NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope, astronomers have discovered two new planetary systems that include three super-Earths in the habitable zone.

Kepler-62f, a super-Earth-size planet in the habitable zone of a star smaller and cooler than the Sun (NASA Ames / JPL-Caltech)
The Kepler-62 planetary system, located about 1,200 light-years from Earth in the constellation Lyra, hosts five exoplanets – 62b, 62c, 62d, 62e and 62f.
Four of them are so-called super-Earths, larger than our own planet, but smaller than even the smallest giant planet in our Solar System.

Kepler-62e, a super-Earth-size planet in the habitable zone of a star smaller and cooler than the Sun (NASA Ames / JPL-Caltech)
These exoplanets have radii of 1.3, 1.4, 1.6, and 1.9 times that of Earth. In addition, one of the five is a roughly Mars-sized planet, half the size of Earth.
According to a paper published online in the journal Science, the two super-Earths in Kepler-62 (62e and 62f) orbit their star at distances where they receive about 41% and 120%, respectively, of the warmth from their star that the Earth receives from the Sun.
The planets are thus in the star’s habitable zone, they have the right temperatures to maintain liquid water on their surfaces and are theoretically hospitable to life. Theoretical modeling suggests that both could be solid, either rocky or rocky with frozen water.

Kepler-62 and the Solar System (NASA Ames / JPL-Caltech)
“This appears to be the best example our team has found yet of Earth-like planets in the habitable zone of a Sun-like star,” said Dr Alan Boss of Carnegie Institution of Washington, co-author of the Science paper reporting the discovery of Kepler-62 exoplanets.
The Kepler-69 system, located about 2,700 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, hosts two planets – 69b and 69c.

Kepler-69c, a super-Earth-size planet in the habitable zone of a star like our Sun (NASA Ames / JPL-Caltech)
Kepler-69c is 70 percent larger than the size of Earth, and orbits in the habitable zone of Kepler-69. Astronomers are uncertain about the composition of this exoplanet, but its orbit of 242 days around a Sun-like star resembles that of our neighboring planet Venus.
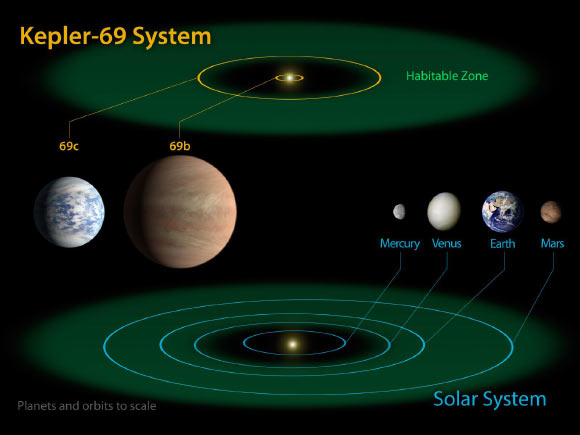
Kepler-69 and the Solar System (NASA Ames / JPL-Caltech)
Astronomers describe the Kepler-69 system in a paper accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal (arXiv.org version).
______
Bibliographic information: William J. Borucki et al. Kepler-62: A Five-Planet System with Planets of 1.4 and 1.6 Earth Radii in the Habitable Zone. Science, published online April 18, 2013; doi: 10.1126/science.1234702
Thomas Barclay et al. 2013. A super-Earth-sized planet orbiting in or near the habitable zone around Sun-like star. ApJ, in press; arXiv: 1304.4941







