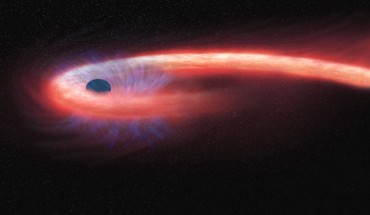
According to a team of astronomers at the University of Sheffield, UK, stars are ripped apart by supermassive black holes 100 times more often than previously thought. This artist’s illustration depicts what astronomers call a tidal disruption event. Image credit: NASA / CXC / M. Weiss. When an unfortunate object, such as a star, wanders too close to a dormant supermassive black hole, the intense gravity of the black hole can destroy the object...