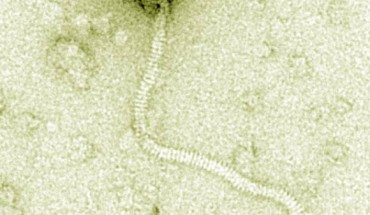
The Tsamsa phage – a giant virus isolated from zebras that died of anthrax in the Namibia’s Etosha National Park – could open up new ways to detect, treat or decontaminate Bacillus anthracis and its relatives that cause food poisoning. Electron microscopy of Tsamsa phage. Scale bar – 100 nm. Image credit: Ganz HH et al. Bacillus anthracis – the anthrax bacterium – forms spores that survive in soil for long periods....