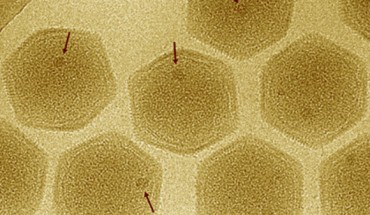
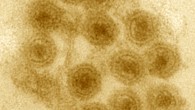
Dr. Albert Erives, a biologist at the University of Iowa, has identified a virus family whose set of genes is similar to that of eukaryotes, an organism classification that includes all plants and animals. The finding is important because it helps clarify how eukaryotes evolved after branching from prokaryotes (single-celled organisms) about two billion years ago. Marseilleviridae particles; arrows indicate ‘large dense bodies.’ Image credit:...