Using the Near-InfraRed Camera (NIRCam) onboard the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have captured a new image of the Red Spider Nebula, a large planetary nebula located in the constellation of Sagittarius.
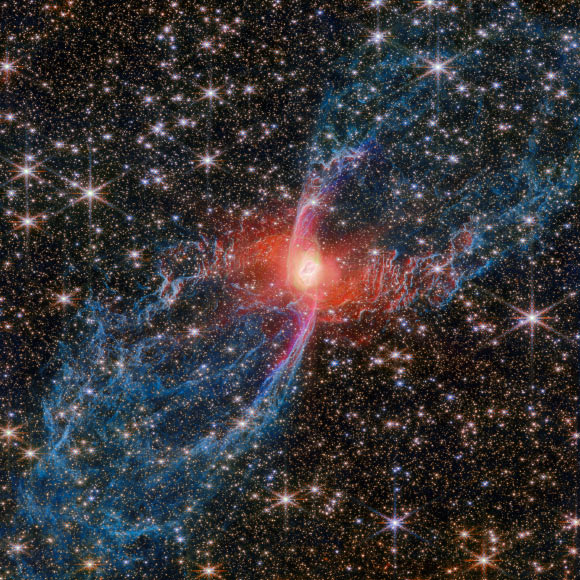

This Webb image shows the Red Spider Nebula. Image credit: NASA / ESA / CSA / Webb / J.H. Kastner, Rochester Institute of Technology.
The Red Spider Nebula was discovered by the American astronomer and physicist Edward Charles Pickering on July 15, 1882.
The object resides around 12,420 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Sagittarius.
Also known as NGC 6537, ESO 590-1 or IRAS 18021-1950, it has a radius of 3.6 light-years.
“Planetary nebulae like the Red Spider Nebula form when ordinary stars like the Sun reach the end of their lives,” the Webb astronomers said in a statement.
“After ballooning into cool red giants, these stars shed their outer layers and cast them into space, exposing their white-hot cores.”
“Ultraviolet light from the central star ionizes the cast-off material, causing it to glow.”
“The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life is as fleeting as it is beautiful, lasting only a few tens of thousands of years.”
“The central star of the Red Spider Nebula is visible in this Webb image, glowing just brighter than the webs of dusty gas that surround it.”
In optical-wavelength images, such as from Hubble, the star appears faint and blue.
But in the NIRCam images, it shows up as red: thanks to its sensitive near-infrared capabilities, Webb has revealed a shroud of hot dust surrounding the central star.
“This hot dust likely orbits the central star, in a disk structure,” the astronomers said.
“Though only a single star is visible in the Red Spider Nebula’s heart, a hidden companion star may lurk there as well.”
“A stellar companion could explain the nebula’s shape, including its characteristic narrow waist and wide outflows.”
“This hourglass shape is seen in other planetary nebulae such as the Butterfly Nebula, which Webb also recently observed.”
“Webb’s new view of the Red Spider Nebula reveals for the first time the full extent of the nebula’s outstretched lobes, which form the ‘legs’ of the spider,” the researchers said.
“These lobes, shown in blue, are traced by light emitted from H2 molecules, which contain two hydrogen atoms bonded together.”
“Stretching over the entirety of NIRCam’s field of view, these lobes are shown to be closed, bubble-like structures that each extend about three light-years.”
“Outflowing gas from the center of the nebula has inflated these massive bubbles over thousands of years.”
“Gas is also actively jetting out from the nebula’s center, as these new Webb observations show.”
“An elongated purple ‘S’ shape centered on the heart of the nebula follows the light from ionized iron atoms.”
“This feature marks where a fast-moving jet has emerged from near the nebula’s central star and collided with material that was previously cast away by the star, sculpting the rippling structure of the nebula seen today.”