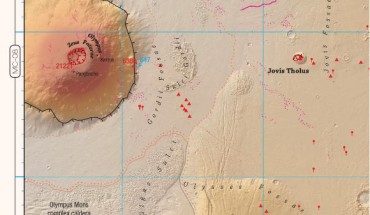
The 84-page atlas of Mars, currently available in English, Hungarian and Czech, was developed as a part of a public outreach project supported by the Europlanet Central European Hub. The map of Tharsis region of Mars from the Pocket Atlas of Mars 36. Image credit: NASA / JPL / GSFC / ESA / DLR / FU / H. Hargitai. “The maps in the new atlas are manually edited, using accurate data from missions and models,” said map editor Dr. Henrik Hargitai,...