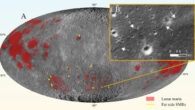
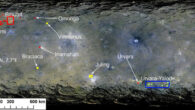
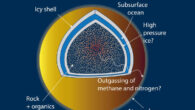
An unexpected phenomenon called convection could help explain many of the volcanoes and other features of the Venusian landscape. Artist’s impression of a volcano erupting on Venus. Image credit: ESA / AOES Medialab. “Nobody had really considered the possibility of convection in the crust of Venus before,” said Washington University in St. Louis Professor Slava Solomatov. “Our calculations suggest that convection is possible and perhaps likely....