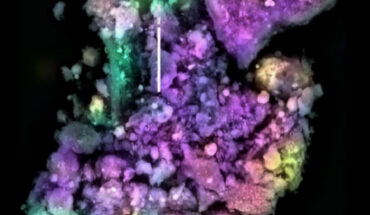
This gum-like material — never seen before in space — was likely formed in the early days of the Solar System, as Bennu’s parent asteroid warmed. Once soft and flexible, but since hardened, the ancient ‘space gum’ consists of polymer-like materials extremely rich in nitrogen and oxygen. Such complex molecules could have provided some of the chemical precursors that helped trigger life on Earth, and finding them in the pristine samples...