A team of astronomers detected a dark spot in the atmosphere of Neptune, in images taken with the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope on May 16, 2016. This confirms the existence of a dark vortex first imaged by Hubble in September 2015 as part of the OPAL (Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy) program.
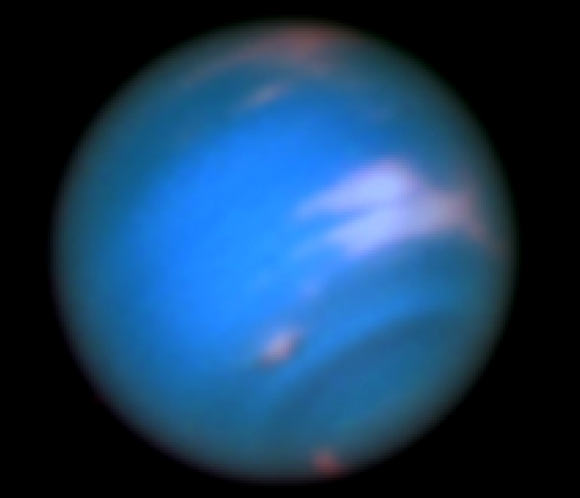
This Hubble image shows Neptune (SDS-2015 resides near and below a patch of bright clouds in the gas giant’s southern hemisphere). Image credit: NASA / ESA / M.H. Wong & J. Tollefson, University of California at Berkeley.
Neptune’s dark vortices are high-pressure systems. They are typically only seen at blue wavelengths, and only Hubble has the high resolution required for seeing them on the distant gas giant.
They are usually accompanied by bright ‘companion clouds,’ which are also now visible on the planet.
The bright clouds form when the flow of ambient air is perturbed and diverted upward over the dark vortex, causing gases to likely freeze into methane ice crystals.
“Dark vortices coast through the atmosphere like huge, lens-shaped gaseous mountains,” said University of California at Berkeley astronomer Dr. Mike Wong, who led the team that analyzed the Hubble images.
“And the companion clouds are similar to so-called orographic clouds that appear as pancake-shaped features lingering over mountains on Earth.”
Dr. Wong and his colleagues provisionally refer to the feature as SDS-2015 (Southern Dark Spot discovered in 2015).
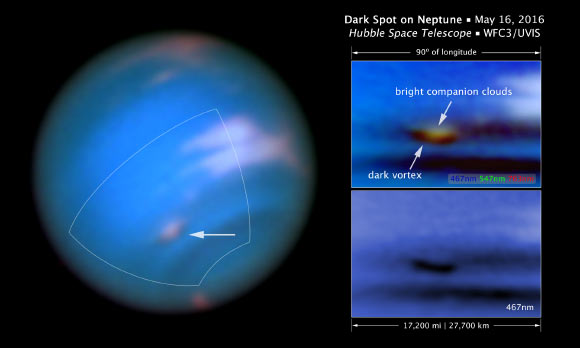
This Hubble image confirms the presence of a dark vortex in the atmosphere of Neptune: the full-color image at top right is a close-up of SDS-2015; the image at bottom right shows that the vortex is best seen at blue wavelengths. Image credit: NASA / ESA / M.H. Wong & J. Tollefson, University of California at Berkeley.
“SDS-2015 was centered at planetographic latitude 45 degrees south in 2015 and at 46 degrees south in 2016, and was observed at longitude about 138 degrees west on May 16, 2016. The width is at least 14 degrees of longitude,” they said.
“Longer-wavelength data reveal the continued presence of bright companion clouds associated with SDS-2015, supporting the interpretation that it is an anti-cyclonic vortex.”
According to the astronomers, SDS-2015 would span the width of the continental United States.
Though similar features were seen during the Voyager 2 flyby of Neptune in 1989 and by Hubble in 1994, SDS-2015 is the first dark vortex observed on Neptune in this century.
The scientists also created a higher-quality map of the vortex and its surroundings.
The discovery was announced in a CBAT (Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams) electronic telegram on May 17.
_____
M.H. Wong et al. 2016. Neptune. Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams, no. 4278