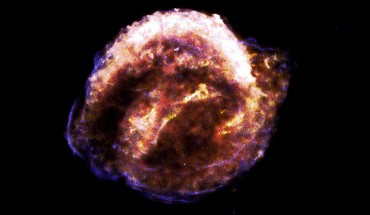
New images from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory show small knots of metal-rich debris in the remnant of Kepler’s supernova, also known as SN 1604, are moving up to 37 million km per hour (23 million mph). These are extremely high speeds for an explosion that happened over 400 years ago as seen from Earth. The Kepler’s supernova remnant. Image credit: NASA / CXC / University of Texas at Arlington / M. Millard et al. The Kepler supernova remnant...