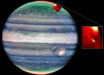
A nova is a cataclysmic event on the surface of a white dwarf star in a binary stellar system that increases the overall brightness by several orders of magnitude. A team of European astronomers has discovered the remains of a nova in a globular cluster called Messier 22.
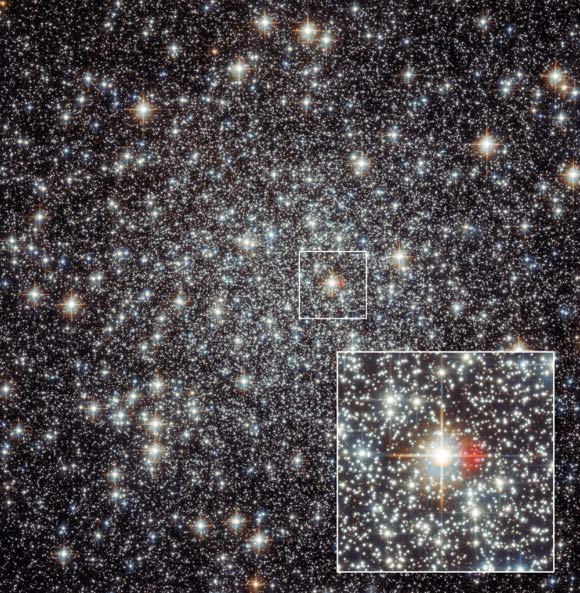

Using the MUSE, an integral-field spectrograph on ESO’s Very Large Telescope, Göttgens et al discovered the remains of a nova near the center of the globular cluster Messier 22. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / F. Göttgens, Institute for Astrophysics, University of Göttingen.
Globular clusters are ancient groups of thousands or even millions of stars, gravitationally bound into a single structure about 100-200 light-years across.
They are among the oldest known objects in the Universe and are relics of the first epochs of galaxy formation.
About 180 such clusters are known to exist around our Milky Way Galaxy.
While there are several observations of novae from extragalactic globular clusters, there have been only two observations in Galactic globular clusters: T Scorpii in the core of Messier 80 and a nova in Messier 14.
The newly-discovered remains of a nova reside in Messier 22, a globular cluster located in the constellation Sagittarius, some 10,400 light-years away.
They form a red nebula of hydrogen gas and other gases, which has a diameter of about 8,000 times the distance between Earth and Sun.
Despite its size, the nebula is relatively light, with a mass about 30 times that of Earth, because the gas was dispersed by the explosion.
“The position and brightness of the remains match an entry from 48 BCE in an ancient collection of observations by Chinese astronomers. They probably saw the original nova in the same place,” said team member Fabian Göttgens, a researcher in the Institute for Astrophysics at the University of Göttingen, Germany.
“With this discovery, this nova may be one of the oldest confirmed extrasolar events recorded in human history.”
The results will be published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
_____
Fabian Göttgens et al. 2019. Discovery of an old nova remnant in the Galactic globular cluster M22. A&A, in press; arXiv: 1904.11515