ESO’s VISTA telescope has created the widest deep view of the sky ever made using infrared light.
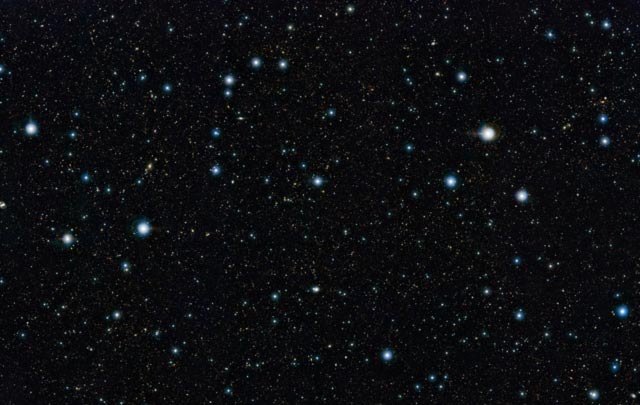

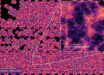
A section of the widest deep view of the sky ever taken using infrared light, with a total effective exposure time of 55 hours. It shows a region of the sky known as the COSMOS field in the constellation of Sextans (ESO / UltraVISTA team / TERAPIX / CNRS / INSU / CASU)
According to the European Southern Observatory (ESO), this new picture of an unremarkable patch of sky comes from the UltraVISTA survey and reveals more than 200 000 galaxies. It forms just one part of a huge collection of fully processed images from all the VISTA surveys that is now being made available by ESO to astronomers worldwide.
The VISTA telescope at ESO’s Paranal Observatory in Chile is the world’s largest survey telescope and the most powerful infrared survey telescope in existence. Since it started work in 2009 most of its observing time has been devoted to public surveys, some covering large parts of the southern skies and some more focused on small areas.
The UltraVISTA survey has been devoted to the COSMOS field, an apparently almost empty patch of sky, which has already been extensively studied using other telescopes, including the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. UltraVISTA is the deepest of the six VISTA surveys by far and reveals the faintest objects.
Data from the VISTA surveys – totaling more than 6 terabytes of images – are now being processed in data centers in the United Kingdom, and in the case of UltraVISTA in France, and are flowing back into the ESO science archive and being made available to astronomers around the world.
At first glance the UltraVISTA image looks unremarkable, a few bright stars and a sprinkling of fainter ones. But in fact almost all of those fainter objects are not stars in the Milky Way, but very remote galaxies, each containing billions of stars.
The expansion of the Universe shifts light from distant objects towards longer wavelengths. For starlight coming from the most distant galaxies that we can observe, this means that most of the light falls in the infrared part of the spectrum when it gets to Earth. As a highly sensitive infrared telescope with a wide field of view, VISTA is uniquely powerful for spotting distant galaxies in the early Universe. By studying galaxies in redshifted light at successively larger distances, astronomers can also trace how galaxies were built up and evolved over the history of the cosmos.
Close inspection of the picture reveals tens of thousands of previously unknown reddish objects scattered between the more numerous cream-colored galaxies. These are mostly very remote galaxies seen when the Universe was only a small fraction of its present age. Early studies of the UltraVISTA images, in combination with images from other telescopes, have revealed the presence of many galaxies that are seen when the Universe was less than a billion years old and a few are seen at even earlier times.
Although the current UltraVISTA image is already the deepest infrared image of its size in existence observations are continuing. The final result, a few years from now, will be significantly deeper still.