Two new papers published in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy provide a summary of therapeutic compounds that showed potential in fighting COVID-19, a novel disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus.
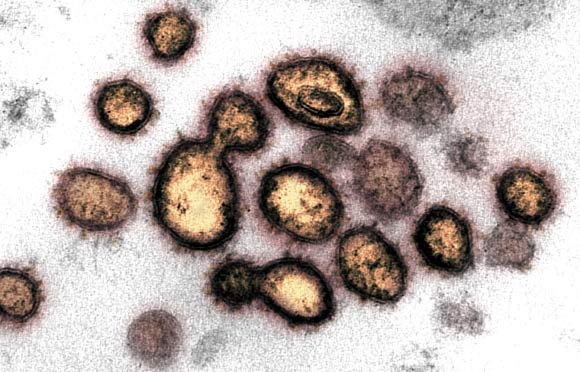
This transmission electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 isolated from a patient in the U.S. Image credit: NIAID-RML.
SARS-CoV-2 is easily transmissible because spike proteins on the virus’ surface bind exceptionally efficiently to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on the surfaces of human cells.
A pilot clinical trial is underway in patients with severe COVID-19, investigating use of recombinant human ACE2 to act as decoys that would attach to spike proteins, disabling SARS-CoV-2’s mechanism for entry into human cells.
The most promising antiviral for fighting SARS-CoV-2 is remdesivir, according to Dr. Miguel Angel Martinez from Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, author of the first paper.
“It gets incorporated into nascent viral RNA, where it prevents RNA synthesis, and in turn, further viral replication,” the researcher explained.
Remdesivir inhibited the replication of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV coronaviruses in tissue cultures, and it displayed efficacy in non-human animal models.
“The clinical condition of the first confirmed case of COVID-19 in the U.S. improved following intravenous remdesivir administration. But more data is needed,” Dr. Martinez said.
Tilorone, a broad spectrum antiviral, may also be active against SARS-CoV-2, according to Dr. Sean Ekins of Collaborations Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Dr. Peter Madrid of SRI International, authors of the second paper.
“Recent observations suggest this 50-year-old synthetic molecule is active against chikungunya virus and MERS-CoV,” they said.
Another approach being researched is the transfusion of blood from recovered patients — which contain antibodies against the virus — into current patients.
Due to lack of high quality randomized clinical trials and knowledge of the precise mechanism of action, it is not clear how effective this therapy is.
It is used mainly in patients in critical condition. Several clinical trials investigating its effectiveness and safety against COVID-19 are now in progress.
More than fifteen vaccine candidates are being developed around the world, which take different approaches to vaccine design. Experts say vaccine development will take approximately 12-18 months.
_____
Miguel Angel Martinez et al. Compounds with therapeutic potential against novel respiratory 2019 coronavirus. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, published online March 9, 2020; doi: 10.1128/AAC.00399-20
Sean Ekins & Peter B. Madrid. Tilorone: A Broad-Spectrum Antiviral for Emerging Viruses. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, published online March 23, 2020; doi: 10.1128/AAC.00440-20