Yuzhoulong qurenensis is one of the earliest-diverging members of the sauropod dinosaur clade Macronaria.
Yuzhoulong qurenensis lived in what is now China during the Middle Jurassic epoch, some 166 million years ago.
The species belongs to Macronaria, a group of sauropod dinosaurs named after the large diameter of the nasal opening in their skull.
“Macronaria is a clade of gigantic body-sized sauropod dinosaurs widely distributed from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous globally,” said senior author Dr. Xin-Xin Ren, a researcher with the Institute of Geology at the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, and colleagues.
“However, its origin, early diversification, and dispersal are still controversial.”
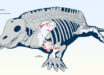
The fossilized remains of a sub-mature individual of Yuzhoulong qurenensis — including a partly preserved skull and 12 dorsal vertebrae — were excavated in Laojun village in southwest China.
The specimens were found in purplish-red silty mudstones located in the middle portion of the Lower Shaximiao Formation.
“Yuzhoulong qurenensis bears a unique combination of features, such as two accessory fossae that exist on the posterior surface of dorsal diapophyses of anterior dorsal vertebrae,” the paleontologists said.

The fossilized bones of Yuzhoulong qurenensis in yellow and another sauropod specimen in blue. Image credit: Dai et al., doi: 10.1098/rsos.220794.
The discovery of Yuzhoulong qurenensis sheds new light on the origin and early diversification of Neosauropoda (a larger clade which includes Macronaria), one of the most controversial topics in the evolution of sauropod dinosaurs.
It suggests that the Middle Jurassic diversity of neosauropods was substantially higher than scientists previously recognized.
It further supports that sauropods achieved a more rapid and varied morphological diversity and paleogeographical dispersal in the Middle Jurassic.
“Although neosauropods lack global distribution in the Middle Jurassic compared with the prosperous distributions of the Late Jurassic, it may suggest the timing of its origin and initial diversification could be as early as the Early Jurassic,” the authors said.
“The most possible widespread dispersal period is in the Bathonian age or earlier when the sea level is relatively low.”
“Anyhow, it further undermines the idea of the East Asia Isolation Hypothesis.”
The team’s paper was published in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
_____
Hui Dai et al. 2022. New macronarian from the Middle Jurassic of Chongqing, China: phylogenetic and biogeographic implications for neosauropod dinosaur evolution. R. Soc. open sci 9 (11): 220794; doi: 10.1098/rsos.220794