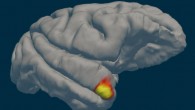
A new long-term study led by Edith Cowan University scientists further supports the hypothesis that coffee intake may be a protective factor against Alzheimer’s disease, with increased coffee consumption potentially reducing cognitive decline. Habitual coffee intake may be a protective factor against Alzheimer’s disease; specifically, increased coffee consumption could contribute to slower cognitive decline potentially by slowing the rate of cerebral...