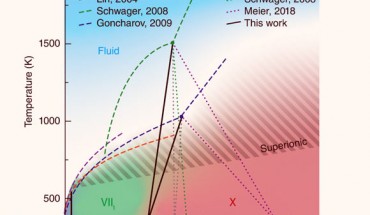
Physicists have observed the transition from a previously known cubic phase, ice VII, to the newly-discovered intermediate, and tetragonal, phase, ice VIIt, before settling into another known phase, ice X. Phase diagram of ice: dark blue-, green-, and red-shaded regions denote ice VII, VIIt and X, respectively, and projected phase boundaries separating high-pressure ice phases from our work are shown as solid black lines; ice X phase boundaries connect...