The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has taken a picture of the galaxy NGC 4424, which is found in the constellation of Virgo.
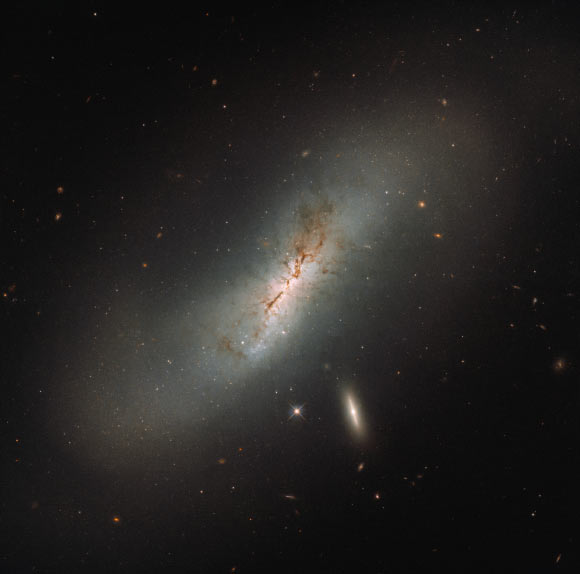

In this Hubble image the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4424 is seen edge on, but from above you would be able to see the arms of the galaxy wrapping around its center to give the characteristic spiral form. The smaller, flatter, bright galaxy sitting just below NGC 4424 is named LEDA 213994. Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble.
Also known as IRAS 12246+0941 and LEDA 40809, NGC 4424 is a barred spiral galaxy.
Approximately 53.8 million light-years from Earth, the galaxy lies in the constellation of Virgo.
It was discovered on February 27, 1865 by the German astronomer Heinrich Louis d’Arrest.
NGC 4424 is considered to be a member of the Virgo Cluster, a collection of almost 2,000 galaxies that stretch across 15 million light-years of space.
This galaxy is believed to be one of the clearest cases for a significant merger in the Virgo Cluster.
It has a strongly disturbed stellar disk, with the banana-shaped stellar distribution and the shell-like stellar features.
Along NGC 4424’s central region, clouds of dust block the light from distant stars and create dark patches.
According to astronomers, NGC 4424 will consume most of its remaining gas during the next 3 billion years; outer stellar structures will fade in the next billion years.
The galaxy will end up as a lenticular galaxy, with smooth stellar disk, little gas and dust in the inner 6,500 light-years, and larger bulge or pseudo-bulge.
In 2012, researchers from the Lick Observatory Supernova Search project observed a Type Ia supernova, called SN 2012cg, in the galaxy.
This image of NGC 4424 (hi-res version) is a composite of separate exposures acquired by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
Three filters — the green filter F555W, the near-infrared filter F814W, and the very broad filter F350LP — were used to sample various wavelengths.
The color results from assigning different hues to each monochromatic image associated with an individual filter.