Striatum, the inner part of the brain, is considered central to decision-making and the development of various addictions. In mouse models and with methods used for mapping cell types and brain tissue, a team of researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden was able to visualize the organization of different opioid-islands in striatum.
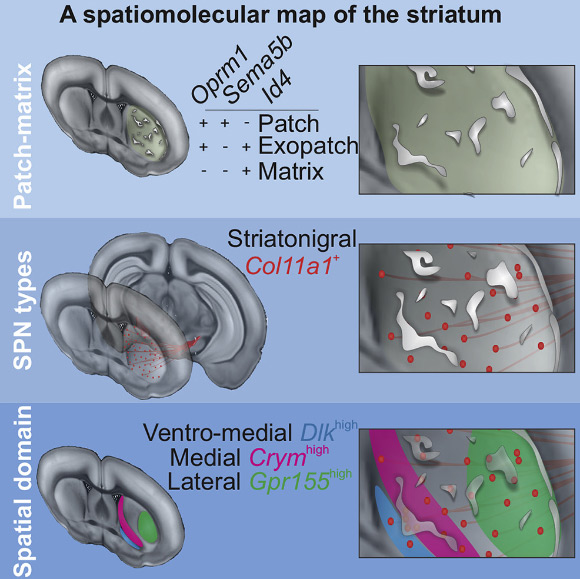
Märtin et al define the molecular identity of striatal projections neurons, focusing on the characterization of the patch and matrix compartments; genetic labeling of mu opioid receptor (Oprm1)-expressing neurons reveals the identity of neuron subtypes, and also establishes spatial markers for the identification of subregions in striatum. Image credit: Märtin et al, doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.096.
In the study, Dr. Konstantinos Meletis and colleagues created a molecular 3D map of the nerve cells targeted by opioids and showed how they are organized in striatum.
“Our map forms the basis for a new understanding of the brain’s probably most important network for decision-making,” Dr. Meletis said.
“It may contribute to an increased understanding of both normal reward processes and the effects of various addictive substances on this network.”
To find this molecular code, the researchers used single-nucleus RNA sequencing, a method to study small differences in individual cells, and mapping of the striatal gene expression.
The results provide the first demonstration of molecular codes that divide the striatum into three main levels of classification: a spatial, a patch-matrix and a cell-type specific organization.
“With this new knowledge we may now begin to analyze the function of different types of nerve cells in different molecularly defined areas,” Dr. Meletis said.
“This is the first step in directly defining the networks’ role in controlling decision-making and addiction with the help of optogenetics.”
“This new knowledge may also form the basis for the development of new treatments based on a mechanistic understanding of the brain’s network,” the scientists said.
The development of the new map of striatum is described in a paper in the journal Cell Reports.
_____
Antje Märtin et al. 2019. A Spatiomolecular Map of the Striatum. Cell Reports 29 (13): 4320-4333; doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.096