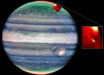
Using the high resolution images from the NIRCam (Near-InfraRed Camera) instrument onboard the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have spotted one of the earliest barred spiral galaxies known, shaping our view of cosmic evolution.
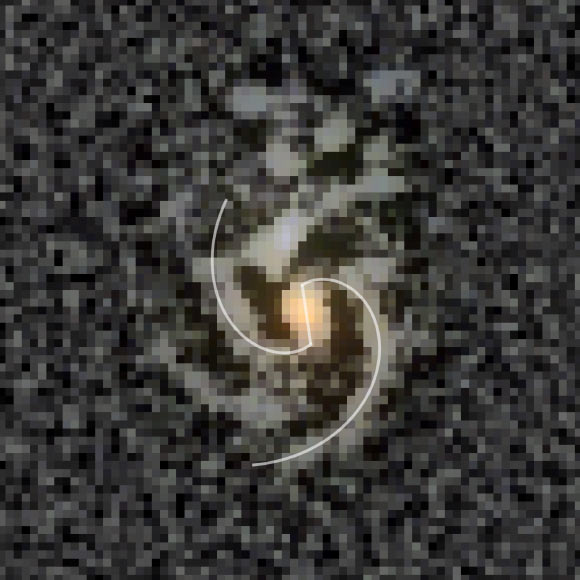

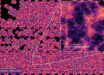
COSMOS-74706: an unsharp mask overlaid onto the F200W, F277W, and F356W filter composition; the white lines are logarithmic spirals fitted to points along the arm structures and a line segment fitted to the approximately North to South aligned bar structure. Image credit: Daniel Ivanov.
Named COSMOS-74706, the newly-discovered barred spiral galaxy existed about 11.5 billion years ago.
“This galaxy was developing bars two billion years after the birth of the Universe,” said Daniel Ivanov, a graduate student at the University of Pittsburgh.
“The defining feature of these galaxies is right in the name: a stellar bar is a linear feature at the center of the galaxy.”
COSMOS-74706’s bar is a dense collection of stars and gas that is aligned in such a way that in images taken perpendicular to a galactic plane, there appears to be a bright line bisecting the galaxy.
Stellar bars can play a role shaping their galaxy’s evolution by funneling gas inward from the outer reaches of a galaxy, feeding the supermassive black hole in the center and dampening star formation throughout the stellar disk.
Other researchers have reported earlier barred spiral galaxies, but the analyses of those are less conclusive because the methods used to analyze the lights’ redshifts are not as definitive as spectroscopy, which was used to validate COSMOS-74706.
In other cases, the galaxy’s light was distorted as it passed by a massive object, a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing.
“In essence, it’s the highest redshift, spectroscopically confirmed, unlensed barred spiral galaxy,” Ivanov said.
“I wasn’t surprised to find a barred spiral galaxy so early in the Universe’s evolution.”
“In fact, some simulations suggest bars forming at redshift 5, or about 12.5 billion years ago.”
“But in principle, I think that this is not an epoch in which you expect to find many of these objects.”
“It helps to constrain the timescales of bar formation. And it’s just really interesting.”
Ivanov and his colleagues reported their discovery on January 8 at the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society.
_____
Daniel Ivanov et al. 2026 An Unlensed Barred Spiral at zspec>3. AAS 247