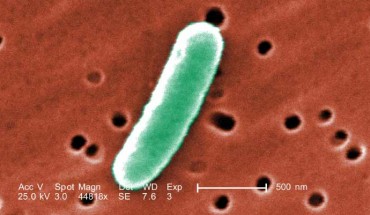
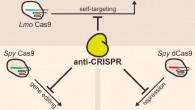
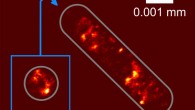
Researchers from the United States, China and France have created what they say is the world’s first stable semi-synthetic microorganism. The research appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. At an extremely high magnification of 44,818x, this colorized scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image reveals some of the morphologic details displayed by Escherichia coli. Image credit: Janice Haney Carr / CDC. Life’s genetic code...