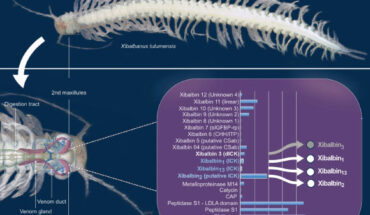
Xibalbanus tulumensis, a venomous remipede found in anchialine caves on the Yucatán Peninsula, is the only crustacean for which a venom system has been described. Xibalbanus tulumensis. Image credit: Pinheiro-Junior et al., doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01955-5. “Venomous animals inject their toxic compounds into other organisms primarily for self-defense or predation,” said Dr. Björn von Reumont, a researcher at Goethe University Frankfurt, and his...