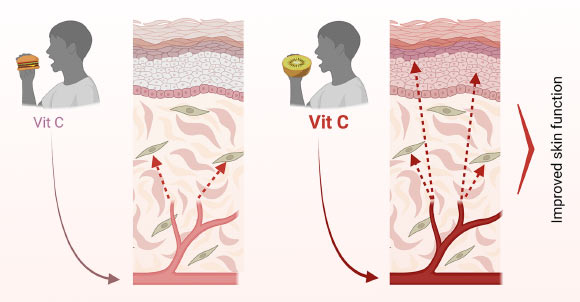
Skin vitamin C levels are closely tied to levels of the vitamin in the blood (plasma) and can be boosted by increasing fruit intake, according to a new study. Carried out on two dozen healthy adults in both New Zealand and Germany, the study shows that boosting plasma levels by consuming two vitamin C-rich kiwifruit per day increases the amount of the vitamin in the skin, improving skin thickness (collagen production) and stimulating renewal and regeneration of the outer skin layer.
Vitamin C (ascorbate) is found in all skin compartments. Pullar et al. carried out a comprehensive investigation to establish the relationship between plasma and skin ascorbate levels, with a focus on the major skin compartments. Image credit: Pullar et al., doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2025.10.587.
“The strength of the association between skin thickness and vitamin C intake is compelling,” said University of Otago’s Professor Margreet Vissers, senior author of the study.
“We were surprised by the tight correlation between plasma vitamin C levels and those in the skin — this was much more marked than in any other organ we have investigated.”
“We are the first to demonstrate that vitamin C in the blood circulation penetrates all layers of the skin and is associated with improved skin function.”
“I am very proud of my team and excited about what the data is telling us.”
The results suggest that beauty really does come from within, supporting your skin function from the inside-out by delivering vitamin C to the skin the way nature designed it — via the bloodstream.
“We know that vitamin C is required for collagen production,”
“This fact has inspired the addition of vitamin C to many skin cream formulations.”
“However, vitamin C is highly water soluble and poorly absorbed through the outer skin barrier.”
“Our study shows that the skin is extremely good at absorbing vitamin C from the blood circulation.”
“Uptake into the outer epidermal skin layer also seems to be prioritized.”
In the study, the authors established the association between plasma and skin vitamin C levels, using healthy skin tissue from patients undergoing elective surgical procedures.
They then involved a before-and-after, dietary vitamin C intervention study at two sites — in Christchurch, New Zealand, and Germany — each with 12 healthy participants.
“All were instructed to consume two kiwifruit daily — the equivalent of 250 micrograms of vitamin C — for eight weeks,” Professor Vissers said.
“We then collected skin samples before and after the intervention, with separate analyses allowing us to look at the skin basal layers in Christchurch and the outer dermal skin layer and skin function tests in Germany.”
The researchers also measured skin sample regeneration — including ultrasound tested measures of skin thickness, elasticity UV protection and renewal of epidermal cells — giving a complete picture of skin function.
“The other really substantial finding showed a significant increase in the participants’ skin thickness levels, reflecting collagen production and an upsurge in the regeneration of their epidermal cells, in other words skin renewal,” Professor Vissers said.
The scientists suggest that increasing your dietary vitamin C intake will result in effective vitamin C uptake into all compartments of the skin.
“The important thing is to keep your plasma levels optimal, which we know can be easily achieved in a healthy person with a vitamin C intake of around 250 mg per day,” Professor Vissers said.
“The body however does not store the vitamin, so we recommend 5+ a day, every day, with one of those five being a high vitamin C food, as a good habit to cultivate.”
The study was published on October 28, 2025 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
_____
Juliet M. Pullar et al. Improved Human Skin Vitamin C Levels and Skin Function after Dietary Intake of Kiwifruit: A High-Vitamin-C Food. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published online October 28, 2025; doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2025.10.587