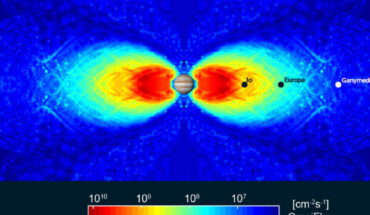
Using data gathered by the Advanced Stellar Compass (ASC) and the Stellar Reference Unit (SRU) onboard NASA’s Juno orbiter, scientists have produced the first complete 3D radiation map of the Jovian system. Along with characterizing the intensity of the high-energy particles near the orbit of the icy moon Europa, the map shows how the radiation environment is sculpted by the smaller moons orbiting near Jupiter’s rings. This graphic shows Juno’s...