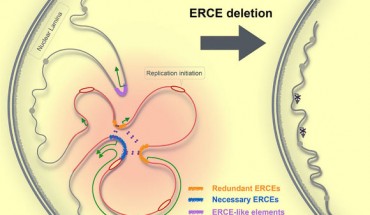
A research team led by Florida State University scientists has demonstrated that there are specific points along the DNA molecule that control replication. The study appears in the journal Cell. Sima et al found that cis-regulatory elements control the 3D compartmentalization, architecture of the genome, and replication timing in a CTCF-independent manner. Image credit: Sima et al, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.036. In cells, DNA and its associated...