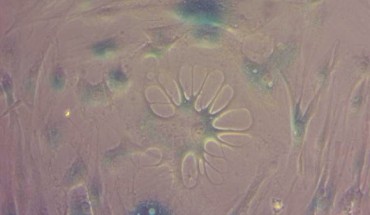
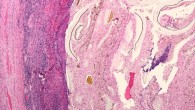
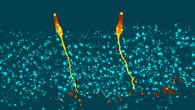
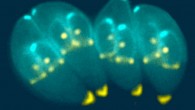
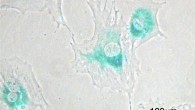
Aging is characterized by a progressive decline of physiological function accompanied by increased incidence of age-related disease. The accumulation of senescent cells is emerging as an important driving factor of the aging process. Senescent cells do not divide, are viable and metabolically active, but have altered physiology. In a study of endothelial cells (which line the inside of blood vessels), University of Exeter’s Professor Lorna Harries...