Sun May Have Escaped Milky Way’s Crowded Core Billions of Years Ago

Using a vast catalog of Sun-like stars built by ESA’s Gaia mission, astronomers have found strong evidence that our home star traveled outward with thousands of stellar counterparts roughly 4 to 6 billion years ago, offering new clues to the formation of the Milky Way’s central bar. An artist’s impression of a migration of the Sun and its stellar twins from the center of the Milky Way approximately...
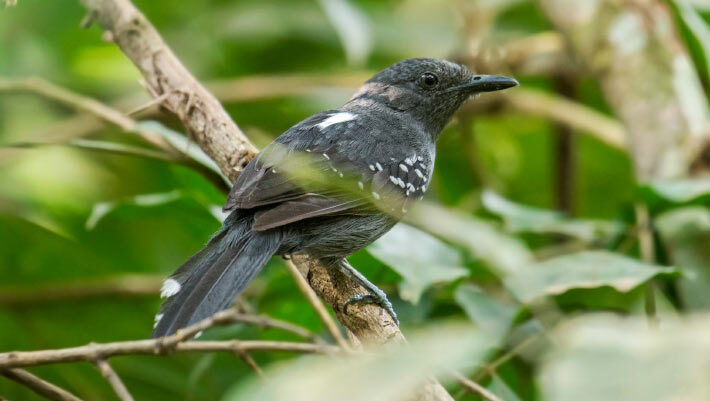







 Two New Bird Species Identified in Amazonia
Two New Bird Species Identified in Amazonia
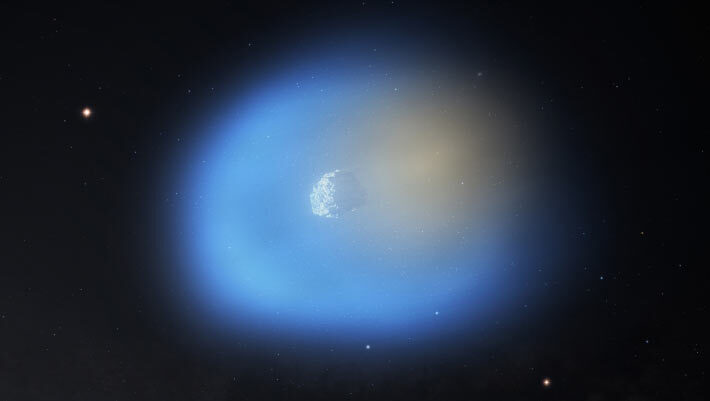
 3I/ATLAS is Unusually Rich in Methanol, ALMA Observations Show
3I/ATLAS is Unusually Rich in Methanol, ALMA Observations Show
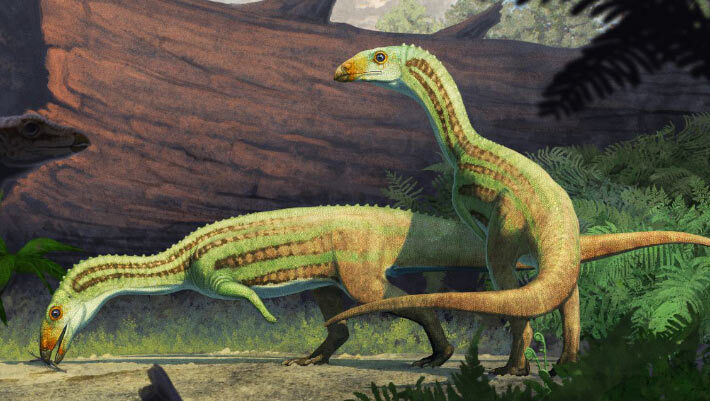
 Triassic Crocodile Relative May Have Learned to Walk on Two Legs
Triassic Crocodile Relative May Have Learned to Walk on Two Legs
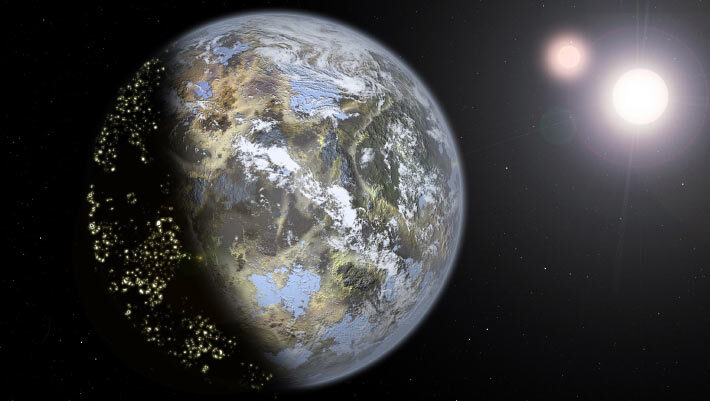
 Stellar ‘Space Weather’ Could Be Blurring Radio Signals from Extraterrestrial Civilizations
Stellar ‘Space Weather’ Could Be Blurring Radio Signals from Extraterrestrial Civilizations
 New Giant Mosasaur Species Discovered in Morocco
New Giant Mosasaur Species Discovered in Morocco
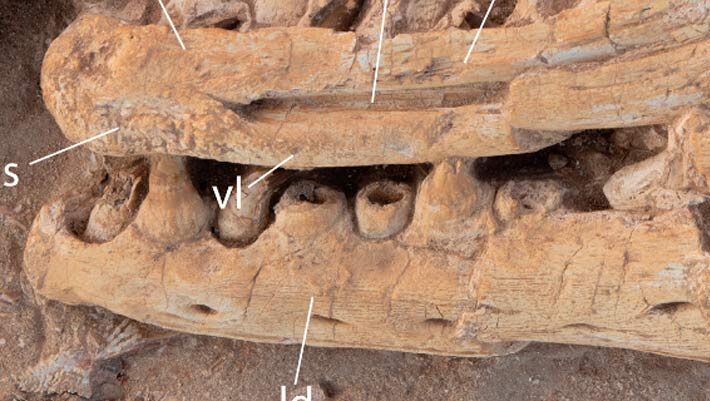
 Graecopithecus May Have Been Partially Bipedal, New Fossil Suggests
Graecopithecus May Have Been Partially Bipedal, New Fossil Suggests